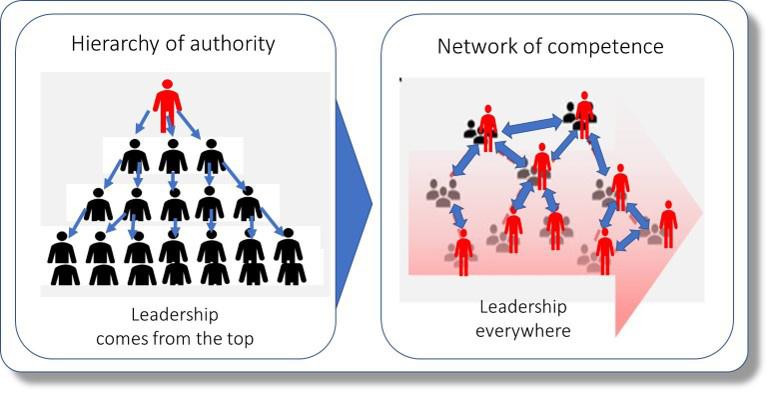
Hierarchy of authority to a network of competence
Steve Denning
Achieving business agility requires an organization to evolve from a hierarchy of authority to a network of competence. That’s because a hierarchy of authority spawns a rash of organizational diseases that undermine business agility.
The Diseases Of Hierarchies Of Authority
Hierarchies of authority lead inevitably to organizational siloes that tend to become barriers to necessary horizontal communication and the sharing of knowledge and data—key features of the agile organization in the digital age. Worse, managers in siloes tend to start promoting the interests of their own silo ahead of the mission of the whole organization, as General Stan McChrystal showed in his book, (Team Of Teams (Portfolio, 2015). The budget also tends to turn into a battle among siloes for their share of the organizational pie. The adversarial process also generates “spend it or lose it” behaviors.
One reason for hanging on to hierarchy is simply habit. Most executives have spent their careers working in steep hierarchies, while submitting to the directives of their bosses, as they climbed up the corporate ladder. Now, having defeated their rivals and having reached the top of the pyramid, it is natural for them to hold on to power as a prize that they have worked hard for, and now won.
But when executives finally get to the top of a big firm, they find themselves overwhelmed. As a comprehensive Harvard Business School survey has revealed, CEOs have “vast, encompassing functional agendas, business unit agendas, multiple organizational levels, and myriad external issues. It also involves a wide array of constituencies—shareholders, customers, employees, the board, the media, government, community organizations, and more.…The job is all-consuming. CEOs are always on, and there is always more to be done…The CEO’s job is relentless.”
Why CEOs Stick Hierarchies Of Authority
Unfamiliarity with network alternatives: CEOs typically inherit a steep hierarchy, and have worked in similar structures most of their career. In some cases, CEOs may not know about the alternative of running the firm as a network. A network may be one in which the network is the formal way in which the firm functions (as at Amazon and Haier) or it may be one which the formal structure is left intact for administrative purposes but the firm actually functions as an informal horizontal network (as at Microsoft and Spotify).
MORE FOR YOU
Ultimately, it’s not what the organization chart says, but how the firm actually operates. It is possible to find both firms traditional pyramidal org charts but acting like a flexible network and firms with apparently networked org charts but in practice behaving like rigid bureaucracies.
Lack of know-how: Another factor is that executives may simply lack know-how to go about creating a network. They could learn from sources such as McChrystal’s Team Of Teams the steps that can taken to move to network mode of operation, including creating a common clearing ground for decision-making communicated in real time, breaking down silos by moving staff from one unit to another so that it becomes not “us vs them” but “us with them.” It can include changing the behavior at the top from that of a fierce commander to more of a gardener nurturing the network.
Lack of goal clarity: A deeper reason is that in many organizations, the overall goal of the organization isn’t clear. In that situation, it would be unwise to move to a network mode of operating until the goal is clarified. For instance the many firms publicly supporting the 2019 declaration of the Business Round Table that the purpose of a firm is to “create value for all the stakeholders” while continuing to give priority in practice to extracting value for shareholders, a network mode of operation would likely lead to mass confusion. While many companies repeat the slogan that “customers are number one,” the statement is often no more than a slogan. As Fred Reichheld will reveal his forthcoming book, Winning on Purpose, (November 2021) less than 20% of major firms are actually giving primacy to the customer. Getting crystal clear on customer primacy is a necessary step towards creating a network of competence.
Lack of measures: A related reason is that even firms trying to give primacy to customers may lack a robust system for actually measuring customer value. At Amazon and Haier, customer value is not just a hope or an aspiration: it is transformed into a measurable accomplishment by formulating and monitoring external measures that keep track of the things that should be happening if the customer is in fact delighted, as well as signaling things that should not be happening if the customer is truly delighted. (These measures need to be established before the activity gets under way.) The actions that the firm needs to take to generate these customer responses also need to be consistently measured and monitored in real time, and the results made transparent throughout the firm.
Having such arrangements in place is what enabled Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos to have sufficient time on his hands to focus mainly on the future: Amazon had systems in place that kept track of what was happening today; so he was not drawn inexorably into the day-to-day decision=making.
By contrast, industrial-era CEOs seem to be almost totally absorbed in what’s happening in the short-term, as different parts of the hierarchy beg for their urgent attention. They are spending almost all the time in internal meetings. The customer hardly enters the picture at all. Only 3% of their time is dedicated to customers.
Misconception of power: A final reason is that CEOs stick to the hierarchy of authority is a misconception of the nature of power. There is a belief that their power comes from being at the summit of a hierarchy and being able to issue directives to subordinates and demand reporting on the status of things. They need to learn that trying to have a finger in every pie is counter-productive: the silos will tend to share the good news but keep the emerging problems to themselves in the hope that the problem will be fixed or go away. The more CEOs try to be the ultimate decision-maker for everything the greater the risk that information will be harder to get. When measurable responsibility and accountability are in place for those actually implementing things, CEOs can focus on their real job: creating the future.
And read also: